There are a number of obstacles to beat previous to reaching mobile reprogramming of pancreatic β cells in vitro and in vivo.
The current research demonstrated that the switch of epigenetic phenotypes was achieved in the cell-free conditioned medium (CM) of pancreatic insulinoma MIN6 cell cultures.
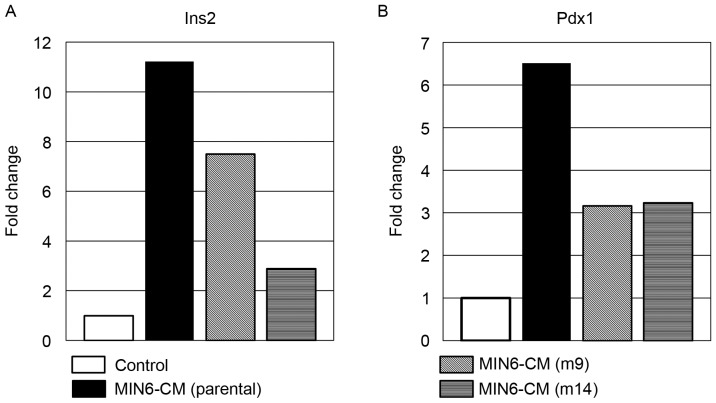
The comparability of a subpopulation of MIN6, m14 and m9 cells indicated that MIN6-m14 cells had been extra liable to mobile reprogramming. Epigenetic profiling revealed that the transcription issue pancreas/duodenum homeobox protein 1 (Pdx1) was differentially related among the many clones.
The culture of differentiated adipocytes in the CM of MIN6-m14 cells resulted in the induction of insulin mRNA expression, and was accompanied by epigenetic occasions of Pdx1 binding.
The epigenetic profiling indicated that Pdx1 is preferentially related to a beforehand uncharacterized area of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) disulfide oxidase, ER oxidoreductin 1 gene.
Therefore, the outcomes of the current research indicated that the CM of MIN6 cells was capable of induce a pancreatic β cell-like phenotype in differentiated adipocytes.
These information present further assist for the utility of cell-free CM for mobile reprogramming.
A modified methodology by differential adhesion and serum-free culture medium for enrichment of most cancers stem cells.
UNASSIGNEDIn this research, we confirmed a modified methodology for the isolation of most cancers stem cells (CSCs) utilizing a mix of differential adhesion methodology and serum-free culture medium (SFM) methodology.
UNASSIGNEDTrypsin-sensitive cells and trypsin-resistant cells had been remoted from MB49, EJ, and SK-OV-Three cells utilizing a mix of differential adhesion methodology and SFM methodology.
The CSCs markers expression of trypsin-resistant cells was verified by the circulate cytometry, the Western blotting, and the quantitative polymerase chain response. Functional comparisons had been verified by the resistance to chemotherapy assay, the transwell assay, and the tumor xenograft formation assay.
UNASSIGNEDTrypsin-resistant cells had been remoted efficiently. They had been recognized with excessive expression of CSCs markers and possessed increased resistance to chemotherapy, larger migration in vitro and stronger tumorigenic skills in vivo.
UNASSIGNEDTrypsin-resistant cells confirmed particular CSCs characterizations. They had been capable of be remoted efficiently with a modified methodology by a mix of differential adhesion methodology and SFM methodology.